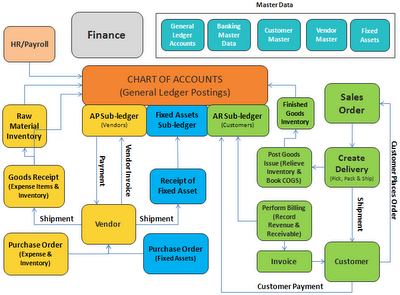
How to become FI/CO Consultant?
Month 1 Step 1 : Watch SAP Computer Based Training Video SAP System Management - System Administration Basic & SAP System Management - System Administration Basic Advanced User + CCMS Step 2 : Study And Practice The Training Manual (9 set) Step 3 : Watch SAP Computer Based Training Video Shipping Clerk, SOP and Structure OP Step 4 : Study And Practice The Training Manual AA, AP, AR, CO-CCA, CO-IO, COPA, CO-PC and GL Month 2 Step 5 : Walk Through SAP Q&A Material Step 6 : Browse Configuration Quick Notes Step 7 : Study The SAP Real-Life Blueprint Documentation (AA, AP, AR, CO dan GL) Month 3 Step 8 : Study The FI/CO Popular Interview Questions And Answers Step 9 : Tips To Behave Like An Experienced Consultant In The Job With Other Consultants Step 10 : Repeat All The Above Steps For Once Step 11 : Now Consider Yourself As An Experienced SAP Consultant And Start Applying For A SAP Job Using Our SAP FI/CO Sample Resume! "If you are struggling in FI module in front of others j...